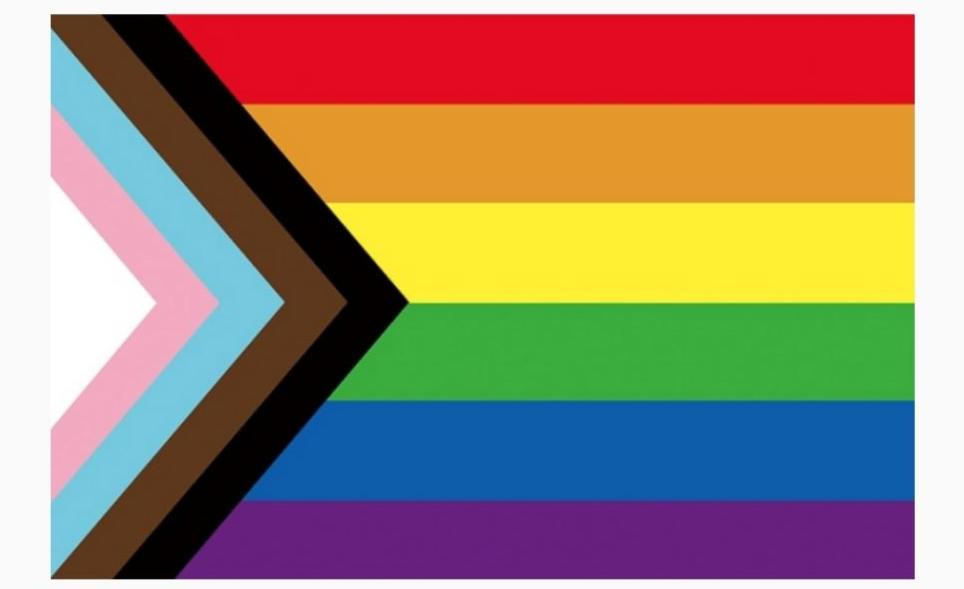
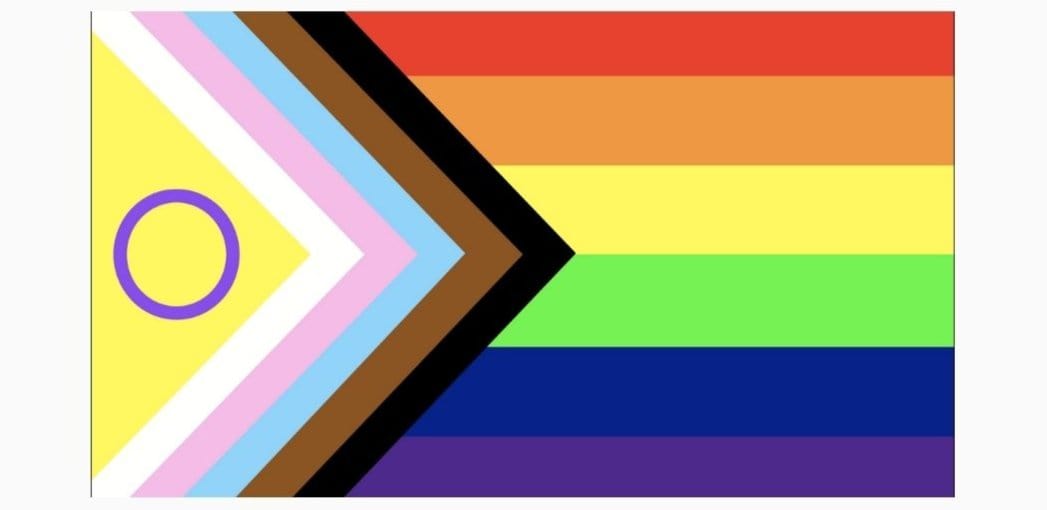
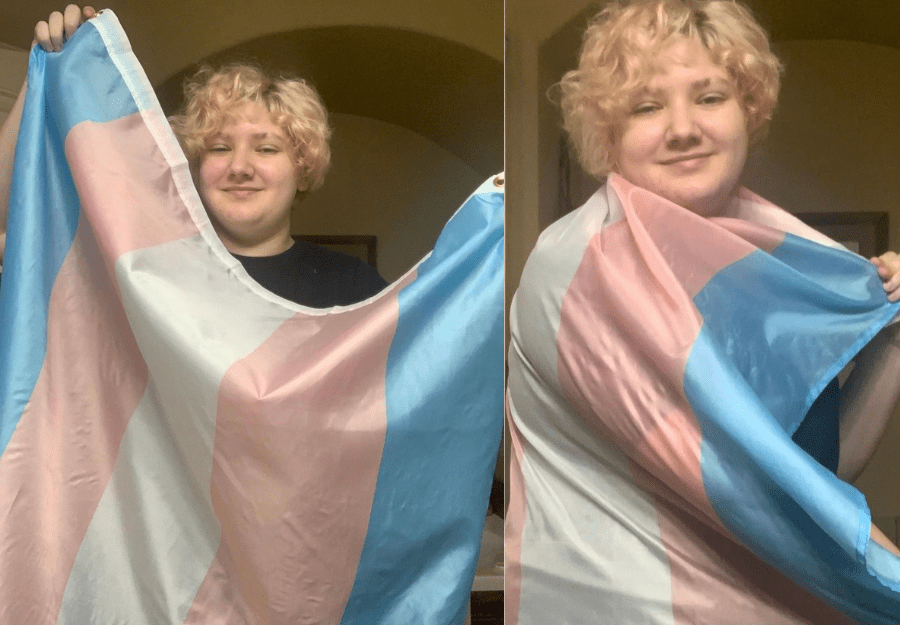
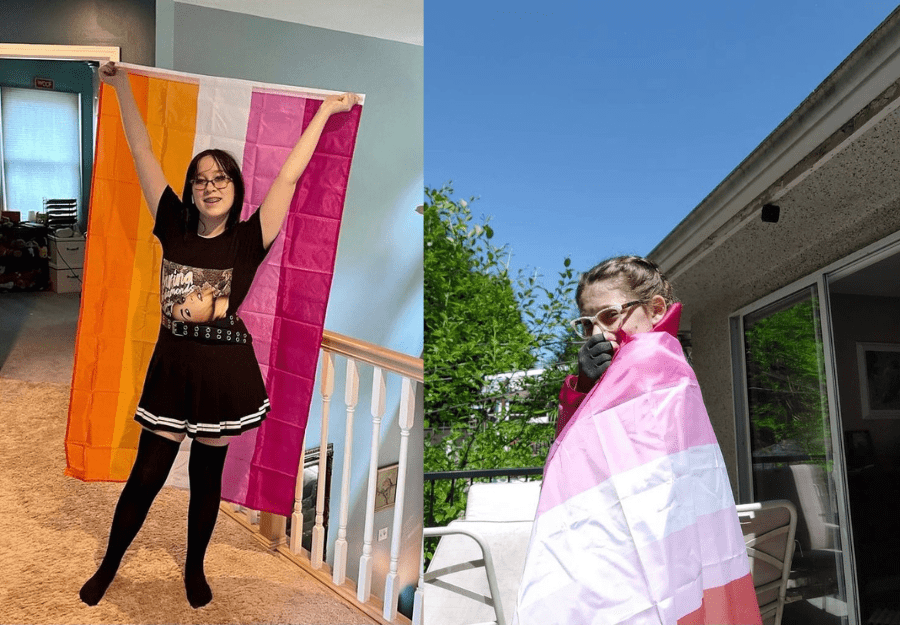
When discussing LGBTQIA+ identities, it's crucial to recognize that not all identities within the community face the same levels of discrimination and exclusion. Marginalized identities refer to those that experience additional layers of oppression and marginalization beyond their sexual orientation or gender identity. Let's delve into the complexities of marginalized LGBTQIA+ identities and the unique challenges they face.
What is Intersectionality?
Intersectionality is a concept that acknowledges how various aspects of a person's identity (such as race, gender, sexuality, and class) intersect and can result in different forms of discrimination and privilege. For example, a non-binary person of color may face discrimination based on both their gender identity and race, leading to a compounded experience of marginalization.
The Invisibility of Non-Binary, Intersex, and Asexual Identities
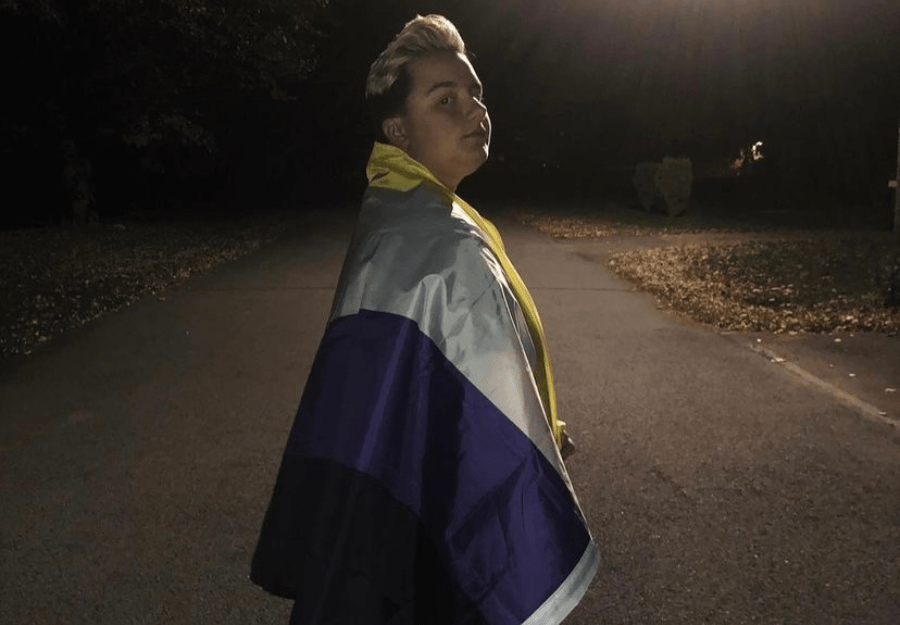
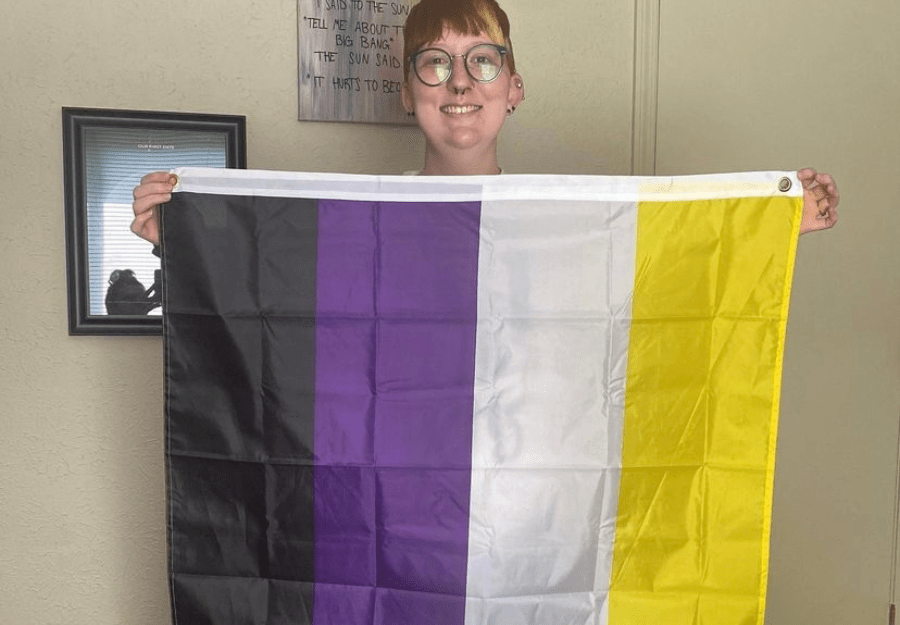
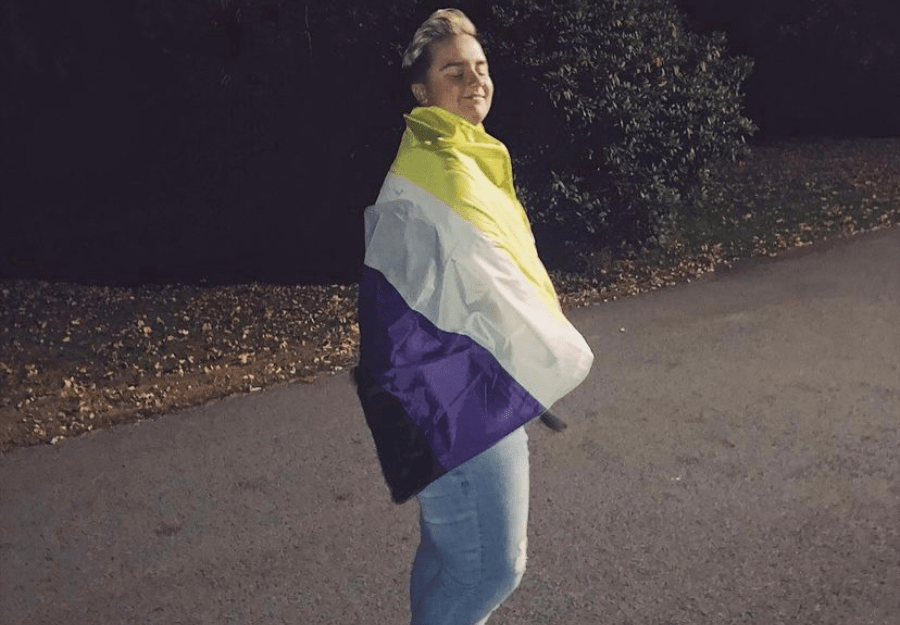
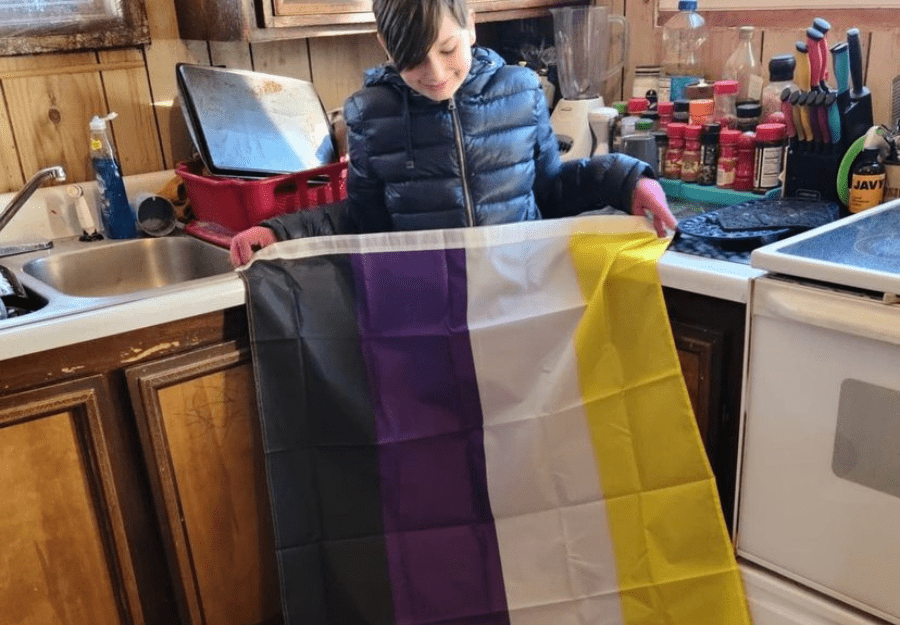
Non-binary, intersex, and asexual individuals are often marginalized within the LGBTQIA+ community due to their identities not conforming to traditional binary norms of gender and sexuality. Non-binary individuals, who do not exclusively identify as male or female, often face challenges in accessing gender-affirming healthcare and navigating public spaces that are not inclusive of non-binary identities.
Intersex individuals, born with variations in sex characteristics that do not fit typical definitions of male or female, have historically faced non-consensual surgeries to conform to binary norms, leading to physical and psychological harm.
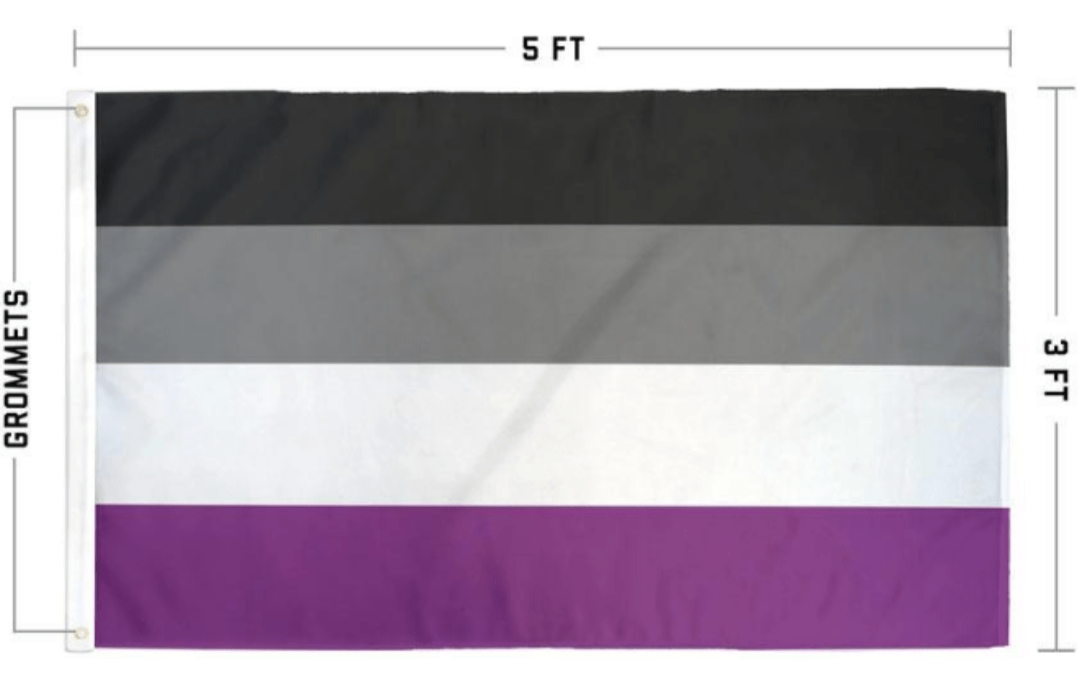
Asexual individuals, who experience little to no sexual attraction, are frequently invalidated or dismissed within society, facing pressure to conform to societal expectations of romantic and sexual relationships.
Historical Marginalization and Recognition Today
Throughout history, non-binary, intersex, and asexual identities have been pathologized, erased, or ignored, contributing to their marginalization. However, there is a growing recognition of these identities within the LGBTQIA+ community and society at large.
Activists and organizations are working to raise awareness about the unique challenges faced by non-binary, intersex, and asexual individuals, advocating for inclusive policies, healthcare, and representation in media and education. By amplifying these voices and experiences, progress is being made towards greater visibility and acceptance of marginalized LGBTQIA+ identities.
Understanding the nuances of marginalized LGBTQIA+ identities is essential in creating a more inclusive and equitable society for all members of the community. By acknowledging and addressing the specific challenges faced by non-binary, intersex, asexual, and other underrepresented identities, we can work towards a more just and affirming world for everyone.